For food companies striving to meet climate targets, Scope 3 emissions are the elephant in the room. These typically account for the majority of a company’s carbon footprint, yet they’re also the most difficult to measure.
That’s where managing Scope 3 through supplier engagement becomes a game-changer.
In this article, we’ll explore why it’s critical for your business and how to get started.
What is supplier engagement?
Supplier engagement is the collaboration between retailers or food companies and their suppliers to measure, report, and reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across the value chain. These emissions often stem from agriculture, processing, transportation, and packaging—areas where suppliers hold the most accurate data.
Unlike one-way data collection, effectively managing Scope 3 through supplier engagement builds a two-way partnership. It involves sharing tools, aligning on standards, and enabling suppliers to provide primary emissions data rather than relying on estimates or outdated averages.
The complexity of Scope 3 emissions & the food supply chain
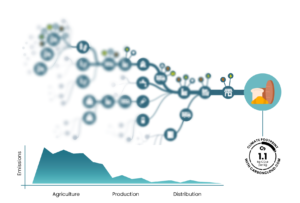
Scope 3 emissions cover a wide range of activities, including the production of goods and services, transportation, waste generation, and more. In the retail sector, much of the carbon footprint is tied to the products they sell, which means it’s spread across a vast and intricate network of suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers. This is particularly true in the food industry, where Scope 3 emissions can contribute up to 70-90% of a company’s total carbon footprint.
The complexity of food supply chains, along with the diverse food production methods—from agriculture to processing and distribution—adds to the difficulty of gathering accurate Scope 3 emissions data.
Calculating these emissions with precision requires input data that is often difficult to obtain, making the process even more challenging. Traditionally, many businesses have attempted to gather Scope 3 emissions data manually, relying on emails, spreadsheets, and surveys.
This approach, while well-intentioned, often leads to incomplete or outdated Scope 3 emission data. Suppliers may struggle to track their own emissions accurately, leading to gaps in information that cascade down the supply chain. The result is fragmented data that lacks the granularity needed to guide meaningful action toward carbon reduction.

Why supplier engagement matters for Scope 3 emissions management
To gather reliable Scope 3 emissions data, supplier engagement is crucial. Here’s why.
1. Data accuracy and granularity
Suppliers are the closest to the production processes that generate emissions. They have access to the most accurate information regarding the carbon footprint of raw materials, manufacturing methods, and transportation logistics. Engaging suppliers to take ownership of their part of the emissions data ensures that the information collected is more precise and detailed.
For example, platforms like CarbonCloud offer solutions that automate the process of requesting climate footprints from suppliers. Rather than relying on static, manually collected data, suppliers can provide primary data that reflects current production methods. This data can then be aggregated to offer a comprehensive view of the retailer’s Scope 3 emissions, without the need for constant back-and-forth communication through emails and manual calculations using spreadsheets
📊 Read more about our tips on getting Scope 3 data, including how to overcome the roadblocks in data collection
2. Increased efficiency through digital infrastructure
Manual methods of gathering Scope 3 emissions data are not only prone to error but are also time-consuming. Retailers often find themselves chasing down suppliers for updates or trying to reconcile different data formats and reporting standards (e.g. ESG). Digital infrastructure, as demonstrated by social networks, has already proven that connectivity between various actors in a system can be seamless. Applying this same logic to food supply chain emissions data can simplify the process dramatically.
By engaging suppliers on digital platforms, data collection becomes more streamlined and automatic. Suppliers can provide their emissions data, which is then instantly updated within the retailer’s system. This minimizes delays and ensures that data remains up to date, a critical factor when producing sustainability reports or responding to financial disclosures that require accurate emissions metrics.
 How can a digital network solve Scope 3 data?
How can a digital network solve Scope 3 data?
The challenge of Scope 3 emissions is rooted in a connectivity issue, with a clear and effective solution: a digital network. This network allows stakeholders across the food supply chain to connect digitally on a platform, facilitating the seamless exchange of crucial emissions data, specifically the climate footprint of each commodity.
The best part? This can be done automatically.
3. Incentivizing improvement and innovation
Once retailers have mapped their Scope 3 emissions, they can identify areas where emissions reductions would have the greatest impact. Supplier engagement offers an opportunity to incentivize them to improve their own carbon performance. Retailers can reward suppliers who make significant efforts in reducing their Scope 3 emissions by continuing to procure from them or by offering premium contracts.
For example, a retailer could choose to source more climate-smart products or ingredients from suppliers that demonstrate low emissions or invest in more sustainable practices. By engaging suppliers in the emissions reporting process, retailers not only improve the quality of their data but also drive meaningful improvements across their supply chain.
4. Creating accountability and ownership
Managing Scope 3 emissions through supplier engagement isn’t just about data—it fosters a sense of accountability and ownership among those contributing to that data. Suppliers are no longer passive participants but active stakeholders in the emissions reduction process.
With platforms like CarbonCloud, suppliers are encouraged to take control of their part of the emissions calculations, improving data transparency and collaboration across the supply chain.
And it pays off. Retailers who embrace this approach are better equipped to meet today’s rising demands of consumers and investors regarding corporate sustainability efforts.
5. Aligning with climate ambitions and reporting requirements
Retailers’ ability to set and meet Scope 3 emissions targets depends significantly on the cooperation and performance of their suppliers. Without supplier engagement, it becomes nearly impossible to align Scope 3 supply chain emissions with the retailer’s climate goals. Engaging suppliers allows retailers to create a more comprehensive emissions map, one that stretches across all tiers of the supply chain.
Moreover, increasing pressure from financial disclosures, such as those required by the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), demands retailers not only collect but actively report their Scope 3 data. With harmonized, real-time data from suppliers, retailers can confidently report on their emissions reduction efforts and demonstrate progress toward their climate goals.
Tip: To dive deeper into the topic, check out our related blog posts Scope 3 emissions in the food industry, Scope 1, 2, 3 emissions, GHG Protocol, Product carbon footprint, Corporate carbon footprint

How to boost supplier engagement for effective Scope 3 emissions reduction
Managing Scope 3 through supplier engagement isn’t just about asking for supply chain emission data—it’s about creating the right conditions for collaboration, trust, and action. Here are a few practical yet effective strategies.
- Start with your most impactful suppliers: Focus efforts on high-emissions or high-spend suppliers first. Prioritization ensures your engagement has the greatest possible climate impact.
- Communicate the “why” clearly: Explain how the emissions data will be used and how it benefits both parties. Transparency builds trust and aligns suppliers with your goals.
- Provide tools and support: Share digital tools, templates, or training to make emissions reporting accessible—especially for smaller suppliers with limited resources.
- Incorporate sustainability into procurement criteria: Reward suppliers who report and reduce their emissions with long-term contracts or benefits.
- Establish feedback loops: Keep suppliers informed about how their data contributes to overall goals and recognize progress to maintain motivation.
- Use digital platforms to automate and simplify: Leverage platforms like CarbonCloud to collect data smarter, faster, and enable ongoing collaboration with your suppliers without the manual overhead.
Conclusion: Managing Scope 3 through supplier engagement is a collaborative effort
Scope 3 emissions represent the largest portion of a retailer’s carbon footprint, and for food companies, they can make up as much as 70-90% of their total emissions.
The complexity of food supply chains and diverse production methods makes collecting accurate data for these emissions a challenge that can only be addressed through close collaboration with suppliers.
By engaging suppliers through digital platforms and incentivizing them to take ownership, retailers can not only improve the granularity and accuracy of their Scope 3 emissions but also drive meaningful reductions in carbon emissions across their entire supply chain.
In the journey toward more sustainable retail operations, supplier engagement is not just a best practice—it’s an essential step. As more companies commit to reducing their environmental impact, the retailers that prioritize supplier engagement for their Scope 3 management will be best positioned to meet both regulatory requirements and customer expectations.
Start managing your Scope 3 with supplier engagement
Not sure what solution fits your business? Our guide breaks down the essential features you need to succeed.
Guide: Choosing the right tool for Scope 3 management
A practical guide for F&B businesses to select a solution that captures accurate Scope 3 data, engages suppliers effectively, and scales with your supply chain.